The Key to Everlasting Youth: Your Own Set of Antioxidants
Anti-aging products are more popular than ever.
Health resides in the cell. If you have healthy cells, you will have healthy tissue and healthy organs. However, the cells of our body have to deal with a host of nasty threats such as viruses, bacteria, and infection. One particularly nasty threat that gets very little attention is free radical damage. But it screams for our attention, sometimes much louder than all the others. Free radical damage causes all aging and disease.
Free radical damage is everywhere in our body due to cellular metabolism. Everyday things such as breathing, eating, and even strenuous exercise naturally cause free radicals to occur. Additionally, we have an increased exposure from pollution, cigarette smoke, drugs, illness and stress. All of these stressors on the body changes cellular metabolism. The changes in this activity of metabolic pathways that are caused by epigenetic downregulation and eventually contribute to humans aging.
A free radical is a molecule with an unpaired electron and the body makes approximately 13 sextillion per day. The molecule is reactive and therefore seeking an electron from another source in order to pair. Essentially it steals the electron from a healthy cell. This initiates an uncontrolled chain reaction that can damage the natural function of the living cell, causing various diseases.
Antioxidants mitigate this reaction by giving an electron to the free radical in order to stop the cell damage. However, when the amount of free radicals in the body is greater than the amount of antioxidants available, oxidative stress occurs:

You know what oxidation looks like: rust on a car or the browning of an apple slice when it is exposed to air (oxygen). Although we don’t feel the changes as they happen, the same thing occurs in the body at the cellular level. Oxidative stress presents itself in our bodies as wrinkles and gray hair. It is also the reason we have disease states.
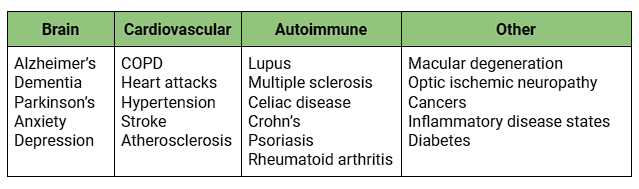
Oxidative stress
from free radical damage is the underlying cause to many diseases:
Oxidative stress in the body can be found through a blood test measuring TBARS (Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances). High levels of this test are associated with cancer, heart disease, stroke, and aging.
For a long time we thought the key to anti-aging and anti-disease was to offset oxidative stress by taking antioxidants such as Vitamins E, C, A, and beta-carotene. And while these external sources might be helpful, scientists have since discovered that our cells make their own antioxidants. If triggered by a messenger (Nrf2), our cells have the ability to go after oxidative stress at the ratio of one million antioxidants to 1 free radical per second, versus a 1:1 ratio of food or vitamins. This is the equivalent to consuming 360 oranges per day!
Nuclear erythroid related factor 2 or Nrf2 (pronounced Nerf two) is the messenger that triggers our own natural antioxidant production. Nrf2 goes to our own DNA and tells it to release all of the cell’s antioxidants so that the body can survive the assault of free radical damage. When we are young, we have a set of Nrf2 messengers that cause our cells to pour out their own antioxidants. It is the reason most people don’t see signs of again until 20 to 25 years of life, and most are fairly resistant to disease.
Since the discovery of Nrf2, scientists have been trying to figure out how to wake up this process inside of the cells for those of us who experience unwanted symptoms of aging. A group of biochemists discovered a synergistic formula of herbs that activates Nrf2 and, in turn, Nrf2 activates the cells’ antioxidants. This is very effective at reducing oxidative stress to almost nothing, even in an eighty-year-old.
I use this formula along with proper nutrition to manage my own health, as do many of my clients who use nutrition to heal from autoimmune disease states. I have also witnessed clients with neurodegenerative diseases decrease, if not eliminate, their symptoms. Even the family dog who suffers from Lyme’s disease can reap amazing results!
Sources:
- Hamilton , K., Reuland, D., and Reuland, D. (2013). The role of nrf2 in the attenuation of cardiovascular disease. Exercise Sports Science Review, (41(3)), 162–8. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e3182948a1e.
- Online resources for disorders caused by oxidative stress. (n.d.). Retrieved from www.oxidativestressresource.org/.
- Natarajan, R., Bogaard, H., Henderson, S., Long, C., Kraskauskas, D., Smithson, L., Ockaili, R., and McCord, J. (2009). Chronic pulmonary artery pressure elevation is insufficient to explain right heart failure. Circulation, (Nov), 1951–60. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULAT IONAHA.109.883843.
- Song, H., Zhang, X., Chen, X., Chen, H., and Rovin , B. (2005). Activation of the nrf2/antioxidant response pathway increases il-8 expression. European Journal of Immunology, 35(Nov), 3258–67.
Don't Miss Out On More!

Heidi Toy FNTP
I help people all over the world heal by identifying and treating the root cause of their body imbalances. Through diet and nutrition, I guide them towards wholeness and balanced lives.
Heidi Toy Functional Medicine Blog















































































































